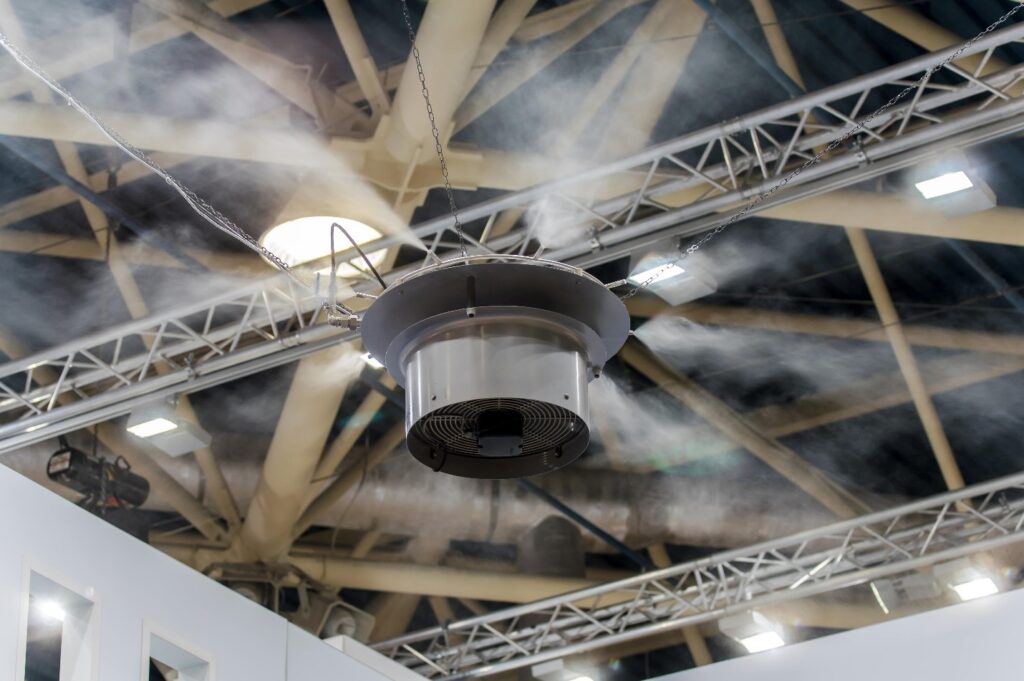
When the sweltering heat strikes, it can bring productivity in industrial settings to a grinding halt. To combat this, you need effective and energy-efficient cooling solutions. Enter evaporative coolers—an ideal choice for managing extreme temperatures without blowing your budget. Global Industrial Port Washington reviews the basics of evaporative cooling, its benefits, and how to choose the right system for your needs.
Understanding Evaporative Cooling
Evaporative cooling operates on a simple yet highly effective principle. It draws in hot air from outside, passes it through water-saturated pads, and then releases cooler air. The process hinges on the evaporation of water, which absorbs heat from the air. This method is particularly effective in open-air environments where traditional air conditioning systems will fall short.
Why Opt for Evaporative Cooling?
- Boosting Productivity: High temperatures can significantly reduce productivity. According to a study by UC Berkeley, for every degree above 71.6°F (22°C), productivity drops by 2%. In large workforces, this can translate into substantial time and financial losses. By maintaining a cooler environment, evaporative coolers help ensure that employees can remain focused and efficient.
- Energy Efficiency: One of the standout features of evaporative coolers is their energy efficiency. Unlike traditional AC units, they become more effective as temperatures rise. This is because hotter air has more energy, leading to more efficient evaporation and cooling. As a result, businesses can save significantly on energy costs, especially during heatwaves.
- Environmental Friendliness: Evaporative coolers use water as a refrigerant, avoiding the harmful chemicals found in traditional AC units. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also ensures a smaller carbon footprint.
- Portability: Many evaporative coolers are portable, allowing you to direct cooling where it’s needed most. This flexibility is invaluable in environments like warehouses, schools, and construction sites, where cooling needs may vary throughout the day.
- Minimal Maintenance: With fewer moving parts and no need for chemical refrigerants, evaporative coolers require less maintenance. This translates into lower costs and less downtime for repairs.
- Humidity Control: Contrary to popular belief, evaporative coolers can be effective in humid environments. They do not create mist or spray water; instead, they use a fan to push air through water-soaked pads, which cools the air without excessively increasing humidity.
Choosing the Right Evaporative Cooler
Selecting the correct evaporative cooler involves understanding the cooling capacity you need, typically measured in Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM). Here’s a quick guide to calculating the required CFM:
- Calculate the Area: Multiply the length and width of the space to get the square footage.
- Determine the Volume: Multiply the square footage by the ceiling height to get the cubic footage.
- Account for Air Changes per Hour (ACH): Multiply the cubic footage by the desired ACH, which is the number of times you want the air to be recirculated in an hour.
- Final Calculation: Divide the result by 60 to get the required CFM.
For example, a room that is 25 feet long, 20 feet wide, and 15 feet high has a volume of 7,500 cubic feet. If you want 4 ACH, the calculation is: 7,500 × 4 / 60 = 500 CFM.
Types of Evaporative Coolers
- Portable Evaporative Coolers: Ideal for smaller areas (up to 6,500 square feet with an 8-9 ft ceiling height), these coolers are perfect for classrooms, office spaces, and small warehouses. Their portability allows them to be moved to different areas as needed.
- Ducted/Whole Building Systems: Best for large, arid environments, these systems are installed outside and connected to the facility’s air ducts. They provide extensive cooling power with significant energy efficiency.
- Window Evaporative Coolers: Easy to install, these coolers fit into open windows, much like traditional window AC units, making them ideal for quick and effective cooling.
- Atomized Evaporative Coolers: These coolers create a fine mist that absorbs heat as it evaporates, cooling large spaces efficiently without creating excessive humidity.
Additional Considerations
- Replacement Pads: To ensure your cooler operates efficiently, be sure to regularly replace the water-saturated pads. The necessary frequency of replacement will depend on the specific unit and its usage.
- Programmable Timers: Many evaporative coolers come with programmable timers, allowing you to control when the unit operates, thus saving energy and extending its lifespan.
- Durability: Evaporative coolers are built to last, with a sturdy design that reduces the likelihood of mechanical failures. This reliability makes them a smart long-term investment.
Evaporative coolers offer a cost-effective, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly solution for managing extreme heat in industrial settings. By understanding how they work and selecting the right type for your needs, you can ensure a comfortable and productive environment for your workforce. Whether you need a portable unit for a small area or a powerful system for a large facility, evaporative cooling has you covered.